ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1
ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1 is an entry-level development board based on ESP32-C6-WROOM-1(U), a general-purpose module with a 8 MB SPI flash. This board integrates complete Wi-Fi, Bluetooth LE, Zigbee, and Thread functions. You can find the board schematic here.
Most of the I/O pins are broken out to the pin headers on both sides for easy interfacing. Developers can either connect peripherals with jumper wires or mount ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1 on a breadboard.
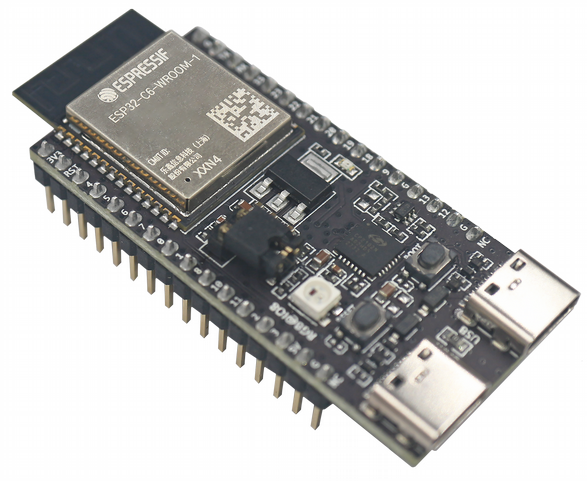
ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1 Board Layout
The block diagram below presents main components of the ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1.
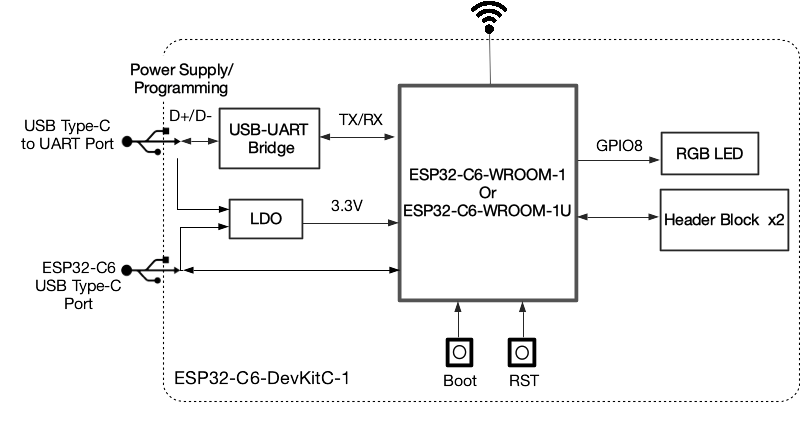
ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1 Electrical Block Diagram
Hardware Components
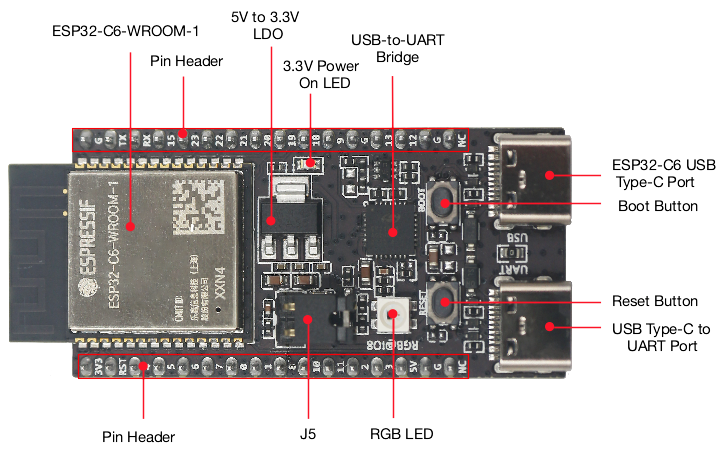
ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1 Hardware Components
Board LEDs
There is one on-board LED that indicates the presence of power. Another WS2812 LED is connected to GPIO8 and is available for software.
Current Measurement
The J5 headers on the ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1 can be used for measuring the current drawn by the ESP32-C6-WROOM-1(U) module:
Remove the jumper: Power supply between the module and peripherals on the board is cut off. To measure the module’s current, connect the board with an ammeter via J5 headers;
Apply the jumper (factory default): Restore the board’s normal functionality.
Note
When using 3V3 and GND pin headers to power the board, please remove the J5 jumper, and connect an ammeter in series to the external circuit to measure the module’s current.
Pin Mapping
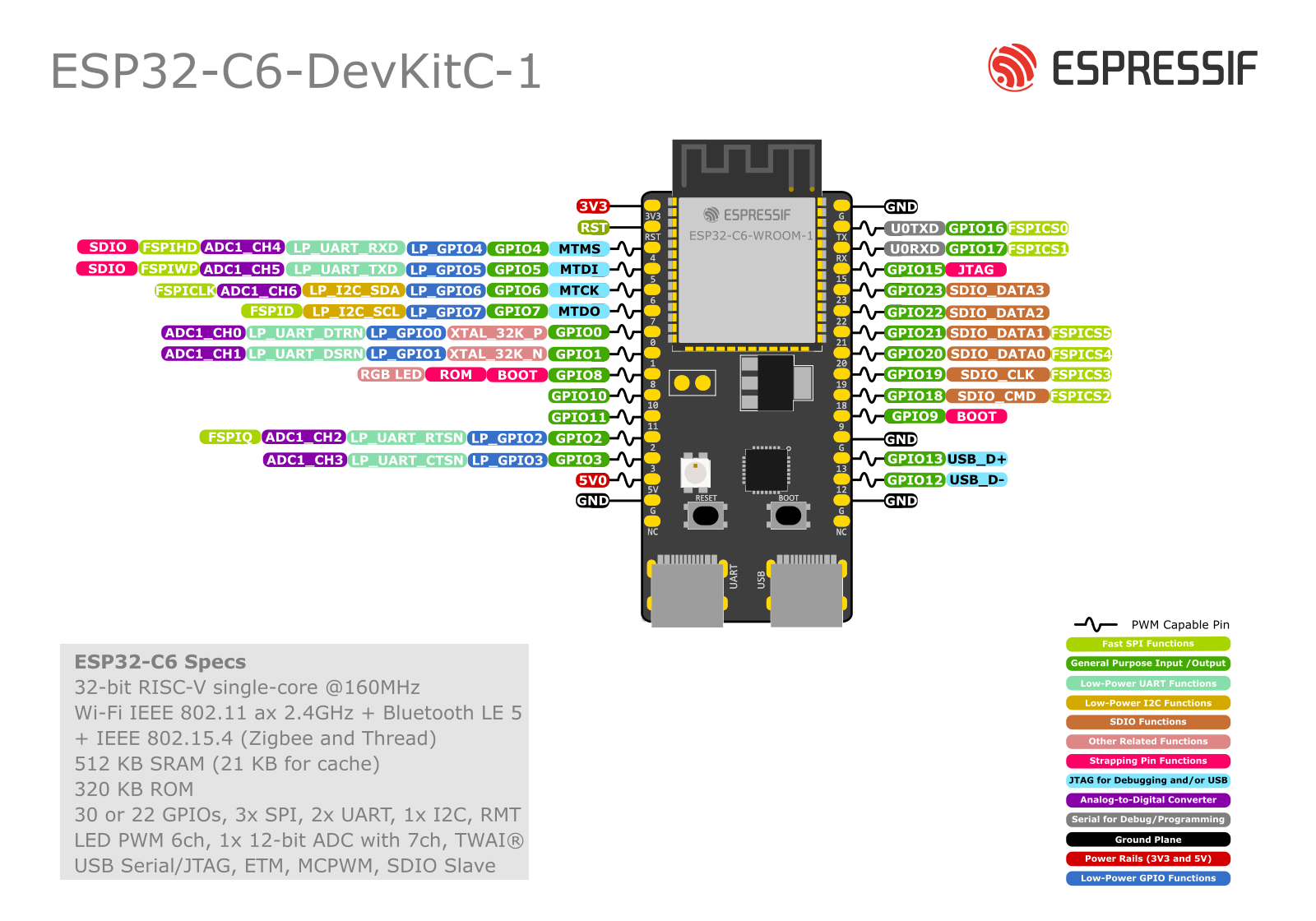
ESP32-C6-DevKitC-1 Pin Layout
Configurations
All of the configurations presented below can be tested by running the following commands:
$ ./tools/configure.sh esp32c6-devkitc:<config_name>
$ make flash ESPTOOL_PORT=/dev/ttyUSB0 -j
Where <config_name> is the name of board configuration you want to use, i.e.: nsh, buttons, wifi…
Then use a serial console terminal like picocom configured to 115200 8N1.
adc
The adc configuration enables the ADC driver and the ADC example application.
ADC Unit 1 is registered to /dev/adc0 with channels 0, 1, 2 and 3 enabled by default.
Currently, the ADC operates in oneshot mode.
More ADC channels can be enabled or disabled in ADC Configuration menu.
This example shows channels 0 and 1 connected to 3.3 V and channels 2 and 3 to GND (all readings show in units of mV):
nsh> adc -n 1
adc_main: g_adcstate.count: 1
adc_main: Hardware initialized. Opening the ADC device: /dev/adc0
Sample:
1: channel: 0 value: 3611
2: channel: 1 value: 3611
3: channel: 2 value: 103
4: channel: 3 value: 104
bmp180
This configuration enables the use of the BMP180 pressure sensor over I2C.
You can check that the sensor is working by using the bmp180 application:
nsh> bmp180
Pressure value = 91531
Pressure value = 91526
Pressure value = 91525
capture
The capture configuration enables the capture driver and the capture example, allowing the user to measure duty cycle and frequency of a signal. Default pin is GPIO 18 with an internal pull-up resistor enabled. When connecting a 50 Hz pulse with 50% duty cycle, the following output is expected:
nsh> cap
cap_main: Hardware initialized. Opening the capture device: /dev/capture0
cap_main: Number of samples: 0
pwm duty cycle: 50 %
pwm frequency: 50 Hz
pwm duty cycle: 50 %
pwm frequency: 50 Hz
coremark
This configuration sets the CoreMark benchmark up for running on the maximum number of cores for this system. It also enables some optimization flags and disables the NuttShell to get the best possible score.
Note
As the NSH is disabled, the application will start as soon as the system is turned on.
crypto
This configuration enables support for the cryptographic hardware and
the /dev/crypto device file. Currently, we are supporting SHA-1,
SHA-224 and SHA-256 algorithms using hardware.
To test hardware acceleration, you can use hmac example and following output
should look like this:
nsh> hmac
...
hmac sha1 success
hmac sha1 success
hmac sha1 success
hmac sha256 success
hmac sha256 success
hmac sha256 success
efuse
This configuration demonstrates the use of the eFuse driver. It can be accessed
through the /dev/efuse device file.
Virtual eFuse mode can be used by enabling CONFIG_ESPRESSIF_EFUSE_VIRTUAL
option to prevent possible damages on chip.
The following snippet demonstrates how to read MAC address:
int fd;
int ret;
uint8_t mac[6];
struct efuse_param_s param;
struct efuse_desc_s mac_addr =
{
.bit_offset = 1,
.bit_count = 48
};
const efuse_desc_t* desc[] =
{
&mac_addr,
NULL
};
param.field = desc;
param.size = 48;
param.data = mac;
fd = open("/dev/efuse", O_RDONLY);
ret = ioctl(fd, EFUSEIOC_READ_FIELD, ¶m);
To find offset and count variables for related eFuse, please refer to Espressif’s Technical Reference Manuals.
gpio
This is a test for the GPIO driver. It uses GPIO1 and GPIO2 as outputs and GPIO9 as an interrupt pin.
At the nsh, we can turn the outputs on and off with the following:
nsh> gpio -o 1 /dev/gpio0
nsh> gpio -o 1 /dev/gpio1
nsh> gpio -o 0 /dev/gpio0
nsh> gpio -o 0 /dev/gpio1
We can use the interrupt pin to send a signal when the interrupt fires:
nsh> gpio -w 14 /dev/gpio2
The pin is configured as a rising edge interrupt, so after issuing the above command, connect it to 3.3V.
To use dedicated gpio for controlling multiple gpio pin at the same time or having better response time, you need to enable CONFIG_ESPRESSIF_DEDICATED_GPIO option. Dedicated GPIO is suitable for faster response times required applications like simulate serial/parallel interfaces in a bit-banging way. After this option enabled GPIO4 and GPIO5 pins are ready to used as dedicated GPIO pins as input/output mode. These pins are for example, you can use any pin up to 8 pins for input and 8 pins for output for dedicated gpio. To write and read data from dedicated gpio, you need to use write and read calls.
The following snippet demonstrates how to read/write to dedicated GPIO pins:
int fd; = open("/dev/dedic_gpio0", O_RDWR);
int rd_val = 0;
int wr_mask = 0xffff;
int wr_val = 3;
while(1)
{
write(fd, &wr_val, wr_mask);
if (wr_val == 0)
{
wr_val = 3;
}
else
{
wr_val = 0;
}
read(fd, &rd_val, sizeof(uint32_t));
printf("rd_val: %d", rd_val);
}
i2c
This configuration can be used to scan and manipulate I2C devices. You can scan for all I2C devices using the following command:
nsh> i2c dev 0x00 0x7f
To use LP_I2C, you can enable ESPRESSIF_LP_I2C0 option. When this option is enabled, LP_I2C operates on GPIO7 as SCL and GPIO6 as SDA. These pins are fixed and cannot be changed. Also enabling LP_I2C will change the default pins of I2C0 due to LP_I2C pin limitation. The default I2C0 pins will be remapped to GPIO23 for SCL and GPIO5 for SDA.
To use slave mode, you can enable ESPRESSIF_I2C0_SLAVE_MODE option. To use slave mode driver following snippet demonstrates how write to i2c bus using slave driver:
#define ESP_I2C_SLAVE_PATH "/dev/i2cslv0"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i2c_slave_fd;
int ret;
uint8_t buffer[5] = {0xAA};
i2c_slave_fd = open(ESP_I2C_SLAVE_PATH, O_RDWR);
ret = write(i2c_slave_fd, buffer, 5);
close(i2c_slave_fd);
}
i2schar
This configuration enables the I2S character device and the i2schar example app, which provides an easy-to-use way of testing the I2S peripheral, enabling both the TX and the RX for those peripherals.
I2S pinout
ESP32-C3 Pin |
Signal Pin |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0 |
MCLK |
Master Clock |
4 |
SCLK |
Bit Clock (SCLK) |
5 |
LRCK |
Word Select (LRCLK) |
18 |
DOUT |
Data Out |
19 |
DIN |
Data In |
After successfully built and flashed, run on the boards’s terminal:
nsh> i2schar
motor
The motor configuration enables the MCPWM peripheral with support to brushed DC motor control.
It creates a /dev/motor0 device with speed and direction control capabilities
by using two GPIOs (GPIO21 and GPIO22) for PWM output. PWM frequency is configurable
from 25 Hz to 3 kHz, however it defaults to 1 kHz.
There is also support for an optional fault GPIO (defaults to GPIO9), which can be used
for quick motor braking. All GPIOs are configurable in menuconfig.
mcuboot_nsh
This configuration is the same as the nsh configuration, but it generates the application
image in a format that can be used by MCUboot. It also makes the make bootloader command to
build the MCUboot bootloader image using the Espressif HAL.
mcuboot_update_agent
This configuration is used to represent an MCUboot image that contains an update agent to perform over-the-air (OTA) updates. Wi-Fi settings are already enabled and image confirmation program is included.
Follow the instructions in the MCUBoot and OTA Update section to execute OTA update.
nsh
Basic configuration to run the NuttShell (nsh).
oa_tc6
This configuration features the network driver for 10BASE-T1S and 10BASE-T1L SPI MAC-PHYs that follow the OPEN Alliance 10BASE-T1x MAC-PHY Serial Interface specification (OA-TC6).
Among such MAC-PHYs are e.g. Microchip LAN865x, Onsemi NCV7410 (NCN26010), Analog Devices ADIN1110.
See the build configuration utility (e.g. make menuconfig) to find out which ones are currently supported.
The OA-TC6 defines a 5 signal connection between the MAC-PHY and the host MCU. These are 4 lines for the standard SPI and 1 line for the interrupt signal from the MAC-PHY to the MCU.
Default pinout
ESP32-C6 Pin |
Signal Pin |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0 |
CS |
SPI Chip Select |
2 |
MISO |
SPI Master In Slave Out |
5 |
INT |
MAC-PHY interrupt signal |
6 |
CLK |
SPI Clock |
7 |
MOSI |
SPI Master Out Slave In |
The oa_tc6 configuration is additionally equipped with the plcatool utility. This allows configuration of the Physical Layer Collision Avoidance (PLCA) functionality
in 10BASE-T1S PHYs.
ostest
This is the NuttX test at apps/testing/ostest that is run against all new
architecture ports to assure a correct implementation of the OS.
pm
This config demonstrate the use of power management.
You can use the pmconfig command to check current power state and time spent in other power states.
Also you can define time will spend in standby and sleep modes:
$ make menuconfig
-> Board Selection
-> (15) PM_STANDBY delay (seconds)
(0) PM_STANDBY delay (nanoseconds)
(20) PM_SLEEP delay (seconds)
(0) PM_SLEEP delay (nanoseconds)
Timer wakeup is not only way to wake up the chip. Other wakeup modes include:
EXT1 wakeup mode: Uses RTC GPIO pins to wake up the chip. Enabled with
CONFIG_PM_EXT1_WAKEUPoption.ULP coprocessor wakeup mode: Uses ULP co-processor to wake up the chip. Enabled with
CONFIG_PM_ULP_WAKEUPoption.GPIO wakeup mode: Uses GPIO pins to wakeup the chip. Only wakes up the chip from
PM_STANDBYmode and requiresCONFIG_PM_GPIO_WAKEUP.UART wakeup mode: Uses UART to wakeup the chip. Only wakes up the chip from
PM_STANDBYmode and requiresCONFIG_PM_GPIO_WAKEUP.
Before switching PM status, you need to query the current PM status to call correct number of relax command to correct modes:
nsh> pmconfig
Last state 0, Next state 0
/proc/pm/state0:
DOMAIN0 WAKE SLEEP TOTAL
normal 0s 00% 0s 00% 0s 00%
idle 0s 00% 0s 00% 0s 00%
standby 0s 00% 0s 00% 0s 00%
sleep 0s 00% 0s 00% 0s 00%
/proc/pm/wakelock0:
DOMAIN0 STATE COUNT TIME
system normal 2 1s
system idle 1 1s
system standby 1 1s
system sleep 1 1s
In this case, needed commands to switch the system into PM idle mode:
nsh> pmconfig relax normal
nsh> pmconfig relax normal
In this case, needed commands to switch the system into PM standby mode:
nsh> pmconfig relax idle
nsh> pmconfig relax normal
nsh> pmconfig relax normal
System switch to the PM sleep mode, you need to enter:
nsh> pmconfig relax standby
nsh> pmconfig relax idle
nsh> pmconfig relax normal
nsh> pmconfig relax normal
Note: When normal mode COUNT is 0, it will switch to the next PM state where COUNT is not 0.
Note: During light sleep, overall current consumption of board should drop from 22mA (without any system load) to 1.3 mA on ESP32-C6 DevkitC-1. During deep sleep, current consumption of module (ESP32-C6-WROOM-1) should drop from 22mA (without any system load) to 48 μA.
pwm
This configuration demonstrates the use of PWM through a LED connected to GPIO8.
To test it, just execute the pwm application:
nsh> pwm
pwm_main: starting output with frequency: 10000 duty: 00008000
pwm_main: stopping output
qencoder —
This configuration demonstrates the use of Quadrature Encoder connected to pins
GPIO10 and GPIO11. You can start measurement of pulses using the following
command (by default, it will open \dev\qe0 device and print 20 samples
using 1 second delay):
nsh> qe
rmt
This configuration configures the transmitter and the receiver of the
Remote Control Transceiver (RMT) peripheral on the ESP32-C6 using GPIOs 8
and 2, respectively. The RMT peripheral is better explained
here,
in the ESP-IDF documentation. The minimal data unit in the frame is called the
RMT symbol, which is represented by rmt_item32_t in the driver:
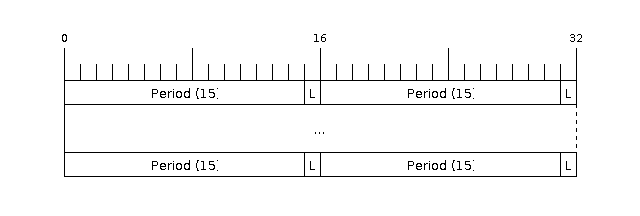
The example rmtchar can be used to test the RMT peripheral. Connecting
these pins externally to each other will make the transmitter send RMT items
and demonstrates the usage of the RMT peripheral:
nsh> rmtchar
WS2812 addressable RGB LEDs
This same configuration enables the usage of the RMT peripheral and the example
ws2812 to drive addressable RGB LEDs:
nsh> ws2812
Please note that this board contains an on-board WS2812 LED connected to GPIO8 and, by default, this config configures the RMT transmitter in the same pin.
romfs
This configuration demonstrates the use of ROMFS (Read-Only Memory File System) to provide
automated system initialization and startup scripts. ROMFS allows embedding a read-only
filesystem directly into the NuttX binary, which is mounted at /etc during system startup.
What ROMFS provides:
System initialization script (
/etc/init.d/rc.sysinit): Executed after board bring-upStartup script (
/etc/init.d/rcS): Executed after system init, typically used to start applications
Default behavior:
When this configuration is used, NuttX will:
Create a read-only RAM disk containing the ROMFS filesystem
Mount the ROMFS at
/etcExecute
/etc/init.d/rc.sysinitduring system initializationExecute
/etc/init.d/rcSfor application startup
Customizing startup scripts:
The startup scripts are located in:
boards/risc-v/esp32c6/common/src/etc/init.d/
rc.sysinit- System initialization scriptrcS- Application startup script
To customize these scripts:
Edit the script files in
boards/risc-v/esp32c6/common/src/etc/init.d/Add your initialization commands using any NSH-compatible commands
Example customizations:
rc.sysinit - Set up system services, mount additional filesystems, configure network.
rcS - Start your application, launch daemons, configure peripherals. This is executed after the rc.sysinit script.
Example output:
*** Booting NuttX ***
[...]
rc.sysinit is called!
rcS file is called!
NuttShell (NSH) NuttX-12.8.0
nsh> ls /etc/init.d
/etc/init.d:
.
..
rc.sysinit
rcS
rtc
This configuration demonstrates the use of the RTC driver through alarms. You can set an alarm, check its progress and receive a notification after it expires:
nsh> alarm 10
alarm_daemon started
alarm_daemon: Running
Opening /dev/rtc0
Alarm 0 set in 10 seconds
nsh> alarm -r
Opening /dev/rtc0
Alarm 0 is active with 10 seconds to expiration
nsh> alarm_daemon: alarm 0 received
sdm
This configuration enables the support for the Sigma-Delta Modulation (SDM) driver which can be used for LED dimming, simple dac with help of an low pass filter either active or passive and so on. ESP32-C6 supports 1 group of SDM up to 4 channels with any GPIO up to user. This configuration enables 1 channel of SDM on GPIO5. You can test DAC feature with following command with connecting simple LED on GPIO5
nsh> dac -d 100 -s 10 test
After this command you will see LED will light up in different brightness.
spi
This configuration enables the support for the SPI driver.
You can test it by connecting MOSI and MISO pins which are GPIO7 and GPIO2
by default to each other and running the spi example:
nsh> spi exch -b 2 "AB"
Sending: AB
Received: AB
If SPI peripherals are already in use you can also use bitbang driver which is a software implemented SPI peripheral by enabling CONFIG_ESPRESSIF_SPI_BITBANG option.
sdmmc_spi
This configuration is used to mount a FAT/FAT32 SD Card into the OS’ filesystem. It uses SPI to communicate with the SD Card, defaulting to SPI2.
The SD slot number, SPI port number and minor number can be modified in Application Configuration → NSH Library.
To access the card’s files, make sure /dev/mmcsd0 exists and then execute the following commands:
nsh> ls /dev
/dev:
console
mmcsd0
null
ttyS0
zero
nsh> mount -t vfat /dev/mmcsd0 /mnt
This will mount the SD Card to /mnt. Now, you can use the SD Card as a normal filesystem.
For example, you can read a file and write to it:
nsh> ls /mnt
/mnt:
hello.txt
nsh> cat /mnt/hello.txt
Hello World
nsh> echo 'NuttX RTOS' >> /mnt/hello.txt
nsh> cat /mnt/hello.txt
Hello World!
NuttX RTOS
nsh>
spiflash
This config tests the external SPI that comes with the ESP32-C6 module connected through SPI1.
By default a SmartFS file system is selected. Once booted you can use the following commands to mount the file system:
nsh> mksmartfs /dev/smart0
nsh> mount -t smartfs /dev/smart0 /mnt
sta_softap
With this configuration you can run these commands to be able to connect your smartphone or laptop to your board:
nsh> ifup wlan1
nsh> dhcpd_start wlan1
nsh> wapi psk wlan1 mypasswd 3
nsh> wapi essid wlan1 nuttxap 1
In this case, you are creating the access point nuttxapp in your board and to
connect to it on your smartphone you will be required to type the password mypasswd
using WPA2.
Tip
Please refer to ESP32 Wi-Fi SoftAP Mode for more information.
The dhcpd_start is necessary to let your board to associate an IP to your smartphone.
timer
This config test the general use purpose timers. It includes the 4 timers, adds driver support, registers the timers as devices and includes the timer example.
To test it, just run the following:
nsh> timer -d /dev/timerx
Where x in the timer instance.
twai
This configuration enables the support for the TWAI (Two-Wire Automotive Interface) driver.
You can test it by connecting TWAI RX and TWAI TX pins which are GPIO0 and GPIO2 by default
to an external transceiver or connecting TWAI RX to TWAI TX pin by enabling
the CONFIG_CAN_LOOPBACK option (Device Drivers -> CAN Driver Support -> CAN loopback mode)
and running the can example:
nsh> can
nmsgs: 0
min ID: 1 max ID: 2047
Bit timing:
Baud: 1000000
TSEG1: 15
TSEG2: 4
SJW: 3
ID: 1 DLC: 1
ulp
This configuration enables the support for the ULP LP core (Low-power core) coprocessor. To get more information about LP Core please check ULP LP Core Coprocessor docs.
Configuration uses a pre-built binary in Documentation/platforms/risc-v/esp32c6/boards/esp32c6-devkitc/ulp_blink.bin
which is a blink example for GPIO0. After flashing operation, GPIO0 pin will blink.
Prebuild binary runs this code:
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "ulp_lp_core_gpio.h"
#define GPIO_PIN 0
#define nop() __asm__ __volatile__ ("nop")
bool gpio_level_previous = true;
int main (void)
{
while (1)
{
ulp_lp_core_gpio_set_level(GPIO_PIN, gpio_level_previous);
gpio_level_previous = !gpio_level_previous;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
nop();
}
}
return 0;
}
usbconsole
This configuration tests the built-in USB-to-serial converter found in ESP32-C6.
esptool can be used to check the version of the chip and if this feature is
supported. Running esptool.py -p <port> chip_id should have Chip is
ESP32-C6 in its output.
When connecting the board a new device should appear, a /dev/ttyACMX on Linux
or a /dev/cu.usbmodemXXX om macOS.
This can be used to flash and monitor the device with the usual commands:
make download ESPTOOL_PORT=/dev/ttyACM0
minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0
watchdog
This configuration tests the watchdog timers. It includes the 1 MWDTS, adds driver support, registers the WDTs as devices and includes the watchdog example application.
To test it, just run the following command:
nsh> wdog -i /dev/watchdogX
Where X is the watchdog instance.
wifi
Enables Wi-Fi support. You can define your credentials this way:
$ make menuconfig
-> Application Configuration
-> Network Utilities
-> Network initialization (NETUTILS_NETINIT [=y])
-> WAPI Configuration
Or if you don’t want to keep it saved in the firmware you can do it at runtime:
nsh> wapi psk wlan0 mypasswd 3
nsh> wapi essid wlan0 myssid 1
nsh> renew wlan0
Tip
Please refer to ESP32 Wi-Fi Station Mode for more information.