Task Trace User Guide
Installation
Install Trace Compass
Task Trace uses the external tool “Trace Compass” to display the trace result.
Download it from https://www.eclipse.org/tracecompass/ and install into the host environment.
After the installation, execute it and choose Tools -> add-ons menu, then select Install Extensions to install the extension named “Trace Compass ftrace (Incubation)”.
NuttX kernel configuration
To enable the task trace function, the NuttX kernel configuration needs to be modified.
The following configurations must be enabled.
CONFIG_SCHED_INSTRUMENTATION: Enables the feature of scheduler notes.CONFIG_SCHED_INSTRUMENTATION_FILTER: Enables the filter logic of the notes.CONFIG_SCHED_INSTRUMENTATION_SYSCALL: Enable system call instrumentation.CONFIG_SCHED_INSTRUMENTATION_IRQHANDLER: Enables IRQ instrumentation.CONFIG_DRIVERS_NOTE: Enables note driver support.CONFIG_DRIVERS_NOTERAM: Enables/dev/notein-memory buffering driver.CONFIG_DRIVERS_NOTECTL: Enables/dev/notectlfilter control driver.CONFIG_SYSTEM_TRACE: Enables “trace” commandCONFIG_SYSTEM_SYSTEM: Enables “system” command (required by trace cmd)
The following configurations are configurable parameters for trace.
CONFIG_SCHED_INSTRUMENTATION_FILTER_DEFAULT_MODESpecify the default filter mode. If the following bits are set, the corresponding instrumentations are enabled on boot.
Bit 0 = Enable instrumentation
Bit 1 = Enable syscall instrumentation
Bit 2 = Enable IRQ instrumentation
Bit 3 = Enable collecting syscall arguments
CONFIG_DRIVERS_NOTE_TASKNAME_BUFSIZESpecify the task name buffer size in bytes. The buffer is used to hold the name of the task during instrumentation. Trace dump can find and show a task name corresponding to given pid in the instrumentation data by using this buffer. If 0 is specified, this feature is disabled and trace dump shows only the name of the newly created task.
CONFIG_DRIVERS_NOTERAM_BUFSIZESpecify the note buffer size in bytes. Higher value can hold more note records, but consumes more kernel memory.
CONFIG_DRIVERS_NOTERAM_DEFAULT_NOOVERWRITEIf enabled, stop overwriting old notes in the circular buffer when the buffer is full by default. This is useful to keep instrumentation data of the beginning of a system boot.
CONFIG_DRIVERS_NOTERAM_CRASH_DUMPIf enabled, it will dump the data in the noteram buffer after a system crash. This function can help to view the behavior of the system before the crash
After the configuration, rebuild the NuttX kernel and application.
If the trace function is enabled, “trace” NSH “Built-In” Applications will be available.
How to get trace data
The trace function can be controlled by “trace” command.
Quick Guide
Getting the trace
Trace is started by the following command.
nsh> trace start
Trace is stopped by the following command.
nsh> trace stop
If you want to get the trace while executing some command, the following command can be used.
nsh> trace cmd <command> [<args>...]
Displaying the trace result
The trace result is accumulated in the memory. After getting the trace, the following command displays the accumulated trace data to the console.
nsh> trace dump
This will get the trace results like the following:
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_close()
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_close -> 0
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_sched_lock()
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_sched_lock -> 0
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_nxsched_get_stackinfo()
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_nxsched_get_stackinfo -> 0
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_sched_unlock()
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_sched_unlock -> 0
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sys_clock_nanosleep()
<noname>-1 [0] 7.640000000: sched_switch: prev_comm=<noname> prev_pid=1 prev_state=S ==> next_comm=<noname> next_pid=0
<noname>-0 [0] 7.640000000: irq_handler_entry: irq=11
<noname>-0 [0] 7.640000000: irq_handler_exit: irq=11
<noname>-0 [0] 7.640000000: irq_handler_entry: irq=15
<noname>-0 [0] 7.650000000: irq_handler_exit: irq=15
<noname>-0 [0] 7.650000000: irq_handler_entry: irq=15
:
By using the logging function of your terminal software, the trace result can be saved into the host environment and it can be used as the input for “Trace Compass”.
If the target has a storage, the trace result can be stored into the file by using the following command. It also can be used as the input for “Trace Compass” by transferring the file in the target device to the host.
nsh> trace dump <file name>
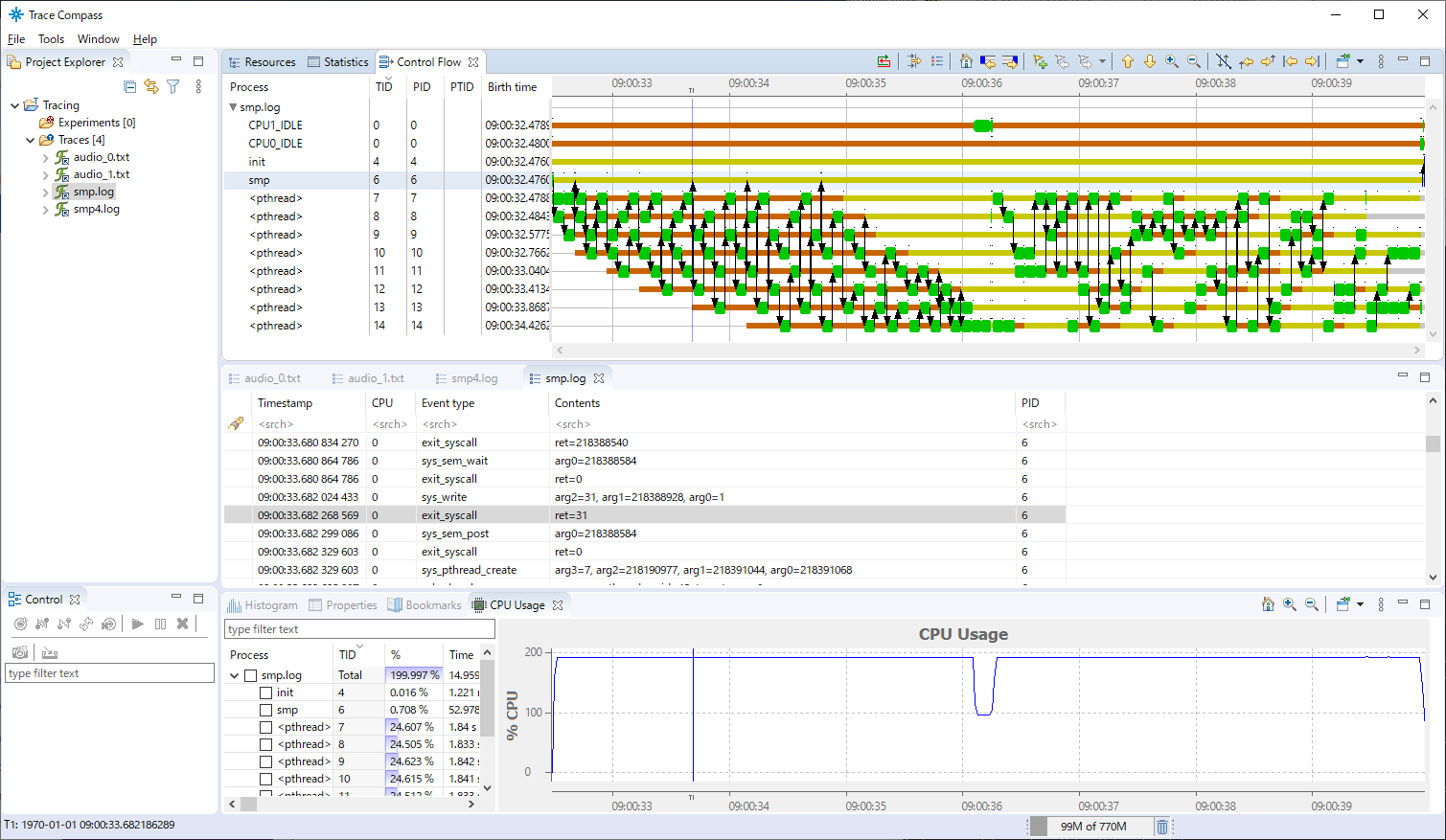
To display the trace result by “Trace Compass”, choose File -> Open Trace menu to specify the trace data file name.
Trace command description
trace start
Start task tracing
Command Syntax:
trace start [-c][<duration>]
-c: Continue the previous trace. The trace data is not cleared before starting new trace.<duration>: Specify the duration of the trace by seconds. Task tracing is stopped after the specified period. If not specified, the tracing continues until stopped by the command.
trace stop
Stop task tracing
Command Syntax:
trace stop
trace cmd
Get the trace while running the specified command.
After the termination of the command, task tracing is stopped.
To use this command, CONFIG_SYSTEM_SYSTEM needs to be enabled.
Command Syntax:
trace cmd [-c] <command> [<args>...]
-c: Continue the previous trace. The trace data is not cleared before starting new trace.<command>: Specify the command to get the task trace.<args>: Arguments for the command.
Example:
nsh> trace cmd sleep 1
trace dump
Output the trace result. If the task trace is running, it is stopped before the output.
Command Syntax:
trace dump [-c][<filename>]
-c: Not stop tracing before the output. Because dumping trace itself is a task activity and new trace data is added while output, the dump will never stop.<filename>: Specify the filename to save the trace result. If not specified, the trace result is displayed to console.
trace mode
Set the task trace mode options.
The default value is given by the kernel configuration CONFIG_SCHED_INSTRUMENTATION_FILTER_DEFAULT_MODE.
Command Syntax:
trace mode [{+|-}{o|s|a|i}...]
+o: Enable overwrite mode. The trace buffer is a ring buffer and it can overwrite old data if no free space is available in the buffer. Enables this behavior.-o: Disable overwrite mode. The new trace data will be disposed when the buffer is full. This is useful to keep the data of the beginning of the trace.+s: Enable system call trace. It records the event of enter/leave system call which is issued by the application. All system calls are recorded by default.trace syscallcommand can filter the system calls to be recorded.-s: Disable system call trace.+a: Enable recording the system call arguments. It records the arguments passed to the issued system call to the trace data.-a: Disable recording the system call arguments.+i: Enable interrupt trace. It records the event of enter/leave interrupt handler which occurred while tracing. All IRQs are recorded by default.trace irqcommand can filter the IRQs to be recorded.-i: Disable interrupt trace.
If no command parameters are specified, display the current mode as the follows.
Example:
nsh> trace mode
Task trace mode:
Trace : enabled
Overwrite : on (+o)
Syscall trace : on (+s)
Filtered Syscalls : 16
Syscall trace with args : on (+a)
IRQ trace : on (+i)
Filtered IRQs : 2
trace syscall
Configure the filter of the system call trace.
Command Syntax:
trace syscall [{+|-}<syscallname>...]
+<syscallname>: Add the specified system call name to the filter. The execution of the filtered system call is not recorded into the trace data.-<syscallname>: Remove the specified system call name from the filter.
Wildcard “*” can be used to specify the system call name.
For example, “trace syscall +sem_*” filters the system calls begin with “sem_”, such as sem_post(), sem_wait(),…
If no command parameters are specified, display the current filter settings as the follows.
Example:
nsh> trace syscall
Filtered Syscalls: 16
getpid
sem_destroy
sem_post
sem_timedwait
sem_trywait
sem_wait
mq_close
mq_getattr
mq_notify
mq_open
mq_receive
mq_send
mq_setattr
mq_timedreceive
mq_timedsend
mq_unlink
trace irq
Configure the filter of the interrupt trace.
Command Syntax:
trace irq [{+|-}<irqnum>...]
+<irqnum>: Add the specified IRQ number to the filter. The execution of the filtered IRQ handler is not recorded into the trace data.-<irqnum>: Remove the specified IRQ number from the filter.
Wildcard “*” can be used to specify all IRQs.
If no command parameters are specified, display the current filter settings as the follows.
Example:
nsh> trace irq
Filtered IRQs: 2
11
15