smf State Machine Framework
Overview
The State Machine Framework (SMF) is a lightweight, application-agnostic framework for implementing finite and hierarchical state machines in NuttX.
SMF provides: - Deterministic state transition semantics - Optional hierarchical state machine (HSM) support - Explicit entry, run, and exit actions - No dynamic memory allocation - Full control over the event loop by the application
The framework is suitable for deeply embedded systems where predictability, low overhead, and explicit control flow are required.
Conceptually, this implementation is a direct port of the SMF originally introduced in Zephyr RTOS, adapted to NuttX coding standards, build system, and documentation conventions.
Architecture
SMF separates responsibilities clearly:
Framework responsibilities - State transitions - Entry/exit sequencing - Hierarchy resolution (LCA) - Termination handling
Application responsibilities - Event acquisition - Event dispatching - State machine scheduling - Data model ownership
This separation ensures that SMF remains fully reusable across applications and execution models.
State Model
Each state is defined by up to three optional callbacks:
Entry action
Run action
Exit action
All actions operate on a user-defined object whose first member is
struct smf_ctx.
struct app_object
{
struct smf_ctx ctx;
/* Application-specific data */
int counter;
bool error;
};
This layout enables zero-cost casting using the SMF_CTX() macro.
State Machine Creation
A state machine is created by defining a table of states that’s indexed by an enum. For example, the following creates three flat states:
enum demo_state
{
STATE_IDLE,
STATE_ACTIVE,
STATE_ERROR,
};
static const struct smf_state demo_states[] = {
[STATE_IDLE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(idle_entry, idle_run, idle_exit, NULL, NULL),
[STATE_ACTIVE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(active_entry, active_run, active_exit, NULL, NULL),
[STATE_ERROR] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(error_entry, error_run, error_exit, NULL, NULL),
};
The example below creates three hierarchical states:
enum demo_state
{
STATE_IDLE,
STATE_ACTIVE,
STATE_ERROR,
};
static const struct smf_state demo_states[] =
{
[STATE_IDLE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(idle_entry, idle_run, idle_exit, parent_idle, NULL),
[STATE_ACTIVE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(active_entry, active_run, active_exit, parent_active, NULL),
[STATE_ERROR] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(error_entry, error_run, error_exit, parent_error, NULL),
};
The next example creates a three-level hierarchical state machine with initial transitions from parent state idle to child state error:
enum demo_state
{
STATE_IDLE,
STATE_ACTIVE,
STATE_ERROR,
};
static const struct smf_state demo_states[] =
{
[STATE_IDLE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(idle_entry, idle_run, idle_exit, NULL, demo_states[STATE_ERROR]),
[STATE_ACTIVE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(active_entry, active_run, active_exit, demo_states[STATE_IDLE], NULL),
[STATE_ERROR] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(error_entry, error_run, error_exit, demo_states[STATE_IDLE], NULL),
};
To set the initial state of the state machine, call smf_set_initial().
To transition between states, call smf_set_state() from entry or run actions.
Note
If CONFIG_SYSTEM_SMF_INITIAL_TRANSITION is not set, smf_set_initial() and smf_set_state() function
should not be passed a parent state as the parent state does not know which child state to transition to.
Transitioning to a parent state is OK if an initial transition to a child state is defined.
A well-formed HSM should have initial transitions defined for all parent states.
Note
While the state machine is running, smf_set_state() should only be called
from the Entry or Run function. Calling smf_set_state() from Exit functions will generate a warning
in the log and no transition will occur.
State Machine Execution
To run the state machine, smf_run_state() function should be called in some application dependent way.
An application should cease calling smf_run_state if it returns a non-zero value.
State Machine Termination
To terminate the state machine, the smf_set_terminate() function should be called.
It can be called from the entry, run, or exit actions.
The function takes a non-zero user defined value that will be returned by the smf_run_state() function.
Retrieving Current State
Leaf State: In the context of a hierarchical state machine, a leaf state is a state that does not contain any child states. It represents the most granular level of state in the hierarchy, where no further decomposition is possible.
Executing State: The executing state refers to the state whose entry, run, or exit action is currently being executed by the state machine. This may be a parent or leaf state, depending on the current operation.
To retrieve the current leaf state, the smf_get_current_leaf_state() function should be called.
For example:
const struct smf_state *leaf_state;
leaf_state = smf_get_current_leaf_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj));
Note
If CONFIG_SYSTEM_SMF_INITIAL_TRANSITION is not enabled, or if the initial state of a parent state is not
defined, always set the state to a leaf state. Otherwise, the state machine may enter a parent state
directly, and smf_get_current_leaf_state() may return a parent state instead of a leaf state.
Ensure initial transitions are properly configured for all parent states to avoid malformed
hierarchical state machines.
To retrieve the state whose entry, run, or exit action is currently being executed,
use the smf_get_current_executing_state() function.
UML State Machines
SMF follows UML hierarchical state machine rules for transitions i.e., the entry and exit actions of the least common ancestor are not executed on transition, unless said transition is a transition to self.
The UML Specification for StateMachines may be found in chapter 14 of the UML specification, available here: https://www.omg.org/spec/UML/
SMF breaks from UML rules in:
Transition actions execute in the source state context, rather than after the exit actions are performed.
Only allowing external transitions to self, not to sub-states. A transition from a superstate to a child state is treated as a local transition.
Prohibiting transitions using
smf_set_state()in exit actions.
SMF also does not provide any pseudostates except the Initial Pseudostate.
Terminate pseudostates can be modelled by calling smf_set_terminate() from the entry action of a
‘terminate’ state. Orthogonal regions are modelled by calling smf_run_state() for each region.
State Machine Examples
Flat State Machine Example
This example turns the following state diagram into code using the SMF, where the initial state is STATE_IDLE.
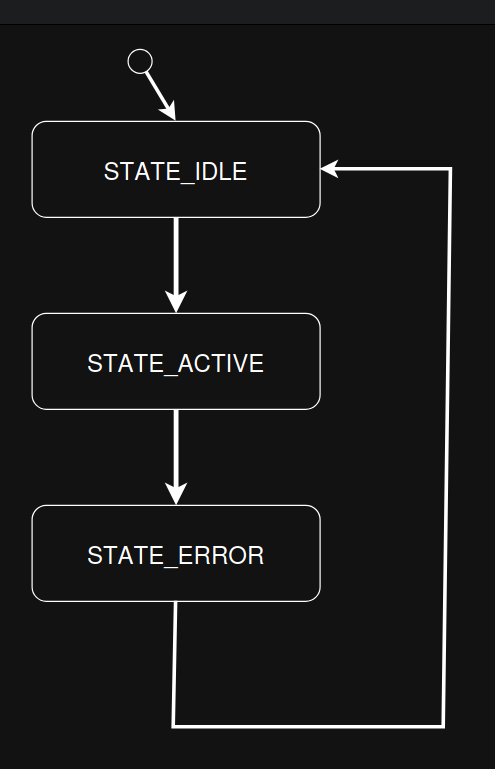
Flat state machine example implemented using SMF.
#include <system/smf.h>
/* Forward declaration of state table */
static const struct smf_state demo_states[];
/* List of demo states */
enum demo_state
{
STATE_IDLE,
STATE_ACTIVE,
STATE_ERROR,
};
/* User defined object */
struct s_object {
/* This must be first */
struct smf_ctx ctx;
/* Other state specific data add here */
} s_obj;
/* State idle */
static void idle_entry(void *o)
{
/* Do something */
}
static enum smf_state_result idle_run(void *o)
{
smf_set_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj), &demo_states[STATE_ACTIVE]);
return SMF_EVENT_HANDLED;
}
static void idle_exit(void *o)
{
/* Do something */
}
/* State active */
static void active_entry(void *o)
{
/* Do something */
}
static enum smf_state_result active_run(void *o)
{
smf_set_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj), &demo_states[STATE_ERROR]);
return SMF_EVENT_HANDLED;
}
static void active_exit(void *o)
{
/* Do something */
}
/* State error */
static void error_entry(void *o)
{
/* Do something */
}
static enum smf_state_result error_run(void *o)
{
smf_set_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj), &demo_states[STATE_IDLE]);
return SMF_EVENT_HANDLED;
}
static void error_exit(void *o)
{
/* Do something */
}
/* Populate state table */
static const struct smf_state demo_states[] = {
[STATE_IDLE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(idle_entry, idle_run, idle_exit, NULL, NULL),
/* State ACTIVE does not have an entry action */
[STATE_ACTIVE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(NULL, active_run, active_exit, NULL, NULL),
/* State ERROR does not have an exit action */
[STATE_ERROR] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(error_entry, error_run, NULL, NULL, NULL),
};
int main(void)
{
int32_t ret;
/* Set initial state */
smf_set_initial(SMF_CTX(&s_obj), &demo_states[STATE_IDLE]);
/* Run the state machine */
while(1) {
/* State machine terminates if a non-zero value is returned */
ret = smf_run_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj));
if (ret) {
/* handle return code and terminate state machine */
break;
}
sleep(1);
}
}
Hierarchical State Machine (HSM)
When CONFIG_SYSTEM_SMF_ANCESTOR_SUPPORT is enabled, states may define a parent.
The example below turns the following state diagram into code using SMF, where IDLE and ACTIVE share a parent
state and IDLE is the initial state.

Hierarchical state machine example implemented using SMF.
Code
#include <system/smf.h>
/* Forward declaration of state table */
static const struct smf_state demo_states[];
/* List of demo states */
enum demo_state { PARENT, IDLE, ACTIVE, ERROR };
/* User defined object */
struct s_object {
/* This must be first */
struct smf_ctx ctx;
/* Other state specific data add here */
} s_obj;
/* Parent State */
static void parent_entry(void *o)
{
/* Do something */
}
static void parent_exit(void *o)
{
/* Do something */
}
/* State IDLE */
static enum smf_state_result idle_run(void *o)
{
smf_set_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj), &demo_states[ACTIVE]);
return SMF_EVENT_HANDLED;
}
/* State ACTIVE */
static enum smf_state_result active_run(void *o)
{
smf_set_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj), &demo_states[ERROR]);
return SMF_EVENT_HANDLED;
}
/* State ERROR */
static enum smf_state_result error_run(void *o)
{
smf_set_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj), &demo_states[IDLE]);
return SMF_EVENT_HANDLED;
}
/* Populate state table */
static const struct smf_state demo_states[] = {
/* Parent state does not have a run action */
[PARENT] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(parent_entry, NULL, parent_exit, NULL, NULL),
/* Child states do not have entry or exit actions */
[IDLE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(NULL, idle_run, NULL, &demo_states[PARENT], NULL),
[ACTIVE] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(NULL, active_run, NULL, &demo_states[PARENT], NULL),
/* State ERROR do not have entry or exit actions and no parent */
[ERROR] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(NULL, error_run, NULL, NULL, NULL),
};
int main(void)
{
int32_t ret;
/* Set initial state */
smf_set_initial(SMF_CTX(&s_obj), &demo_states[IDLE]);
/* Run the state machine */
while(1) {
/* State machine terminates if a non-zero value is returned */
ret = smf_run_state(SMF_CTX(&s_obj));
if (ret) {
/* handle return code and terminate state machine */
break;
}
sleep(1);
}
}
When designing hierarchical state machines, the following should be considered:
Ancestor entry actions are executed before the sibling entry actions. For example, the parent_entry function is called before the
idle_entryfunction.Transitioning from one sibling to another with a shared ancestry does not re-execute the ancestor’s entry action or execute the exit action. For example, the parent_entry function is not called when transitioning from IDLE to ACTIVE, nor is the parent_exit function called.
Ancestor exit actions are executed after the exit action of the current state. For example, the idle_exit function is called before the parent_exit function is called.
The parent_run function only executes if the child_run function does not call either
smf_set_state()or returnSMF_EVENT_HANDLED.Avoid malformed hierarchical state machines by ensuring the state always transitions to a leaf state when
CONFIG_SYSTEM_SMF_INITIAL_TRANSITIONis not enabled, or when a parent state’s initial state is undefined.
Initial Transitions
If CONFIG_SYSTEM_SMF_INITIAL_TRANSITION is enabled, a parent state may define an
initial child state.
static const struct smf_state demo_states[] =
{
[STATE_PARENT] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(parent_entry, NULL, parent_exit, NULL, &demo_states[STATE_CHILD_A]),
[STATE_CHILD_A] = SMF_CREATE_STATE(NULL, child_a_run, NULL, &demo_states[STATE_PARENT], NULL),
};
When entering STATE_PARENT, the framework automatically transitions to
STATE_CHILD_A.
Note
Without initial transition support enabled, applications must always transition directly to a leaf state.
State Execution Model
The application controls execution explicitly.
Set the initial state using
smf_set_initial()Call
smf_run_state()from an event loopStop execution when a non-zero value is returned
smf_set_initial(SMF_CTX(&app), &demo_states[STATE_IDLE]);
while (1)
{
int32_t rc = smf_run_state(SMF_CTX(&app));
if (rc != 0)
{
break;
}
/* Block, poll, or wait for an event */
}
State Run Semantics
The run action returns:
SMF_EVENT_HANDLED– event consumedSMF_EVENT_PROPAGATE– propagate to parent (HSM only)
If smf_set_state() is called, propagation stops immediately.
State Transitions
Transitions are requested explicitly by calling smf_set_state() from
entry or run actions.
static enum smf_state_result active_run(void *obj)
{
struct s_object *s = (struct s_object *)obj;
if (s->error)
{
smf_set_state(SMF_CTX(s), &demo_states[STATE_ERROR]);
return SMF_EVENT_HANDLED;
}
return SMF_EVENT_HANDLED;
}
Calling smf_set_state() from exit actions is rejected by design.
Termination
To terminate a state machine, call smf_set_terminate().
smf_set_terminate(SMF_CTX(&app), -ECANCELED);
The value passed is returned by smf_run_state() and can be used to signal
the termination reason.
State Introspection
SMF exposes two helper APIs:
smf_get_current_leaf_state()smf_get_current_executing_state()
These functions are primarily intended for diagnostics, logging, and testing.
UML Compliance
SMF follows UML hierarchical state machine semantics:
Entry/exit actions execute according to the least common ancestor (LCA)
Self-transitions execute full exit/entry sequences
Local transitions are supported implicitly
Differences from UML:
Transition actions execute in the source state context
Only external self-transitions are supported
No explicit terminate pseudostate
Notes and Constraints
SMF performs no dynamic allocation
State tables are typically
static constThread safety is the responsibility of the application
One SMF instance represents one execution region
Orthogonal regions require multiple SMF instances
Configuration Options
CONFIG_SYSTEM_SMFCONFIG_SYSTEM_SMF_ANCESTOR_SUPPORTCONFIG_SYSTEM_SMF_INITIAL_TRANSITION
Code Location
apps/system/smf– Framework implementationapps/include/system/smf.h– Public API