Adafruit QT Py RP2040
The QT Py RP2040 is a tiny general purpose RP2040 board supplied by Adafruit.
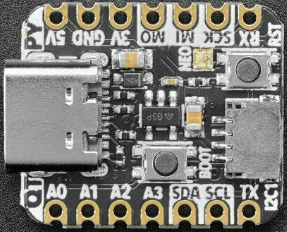
See the Adafruit website for information about the Adafruit QT Py RP2040.
Features
RP2040 microcontroller chip
Dual-core ARM Cortex M0+ processor, flexible clock running up to 133 MHz
264kB of SRAM, and 8MB of on-board Flash memory
Castellated module allows soldering direct to carrier boards
USB Host and Device support via type C connector.
Low-power sleep and dormant modes
Drag & drop programming using mass storage over USB
13 multi-function GPIO pins (11 breakout pads and two QT pads)
2× SPI, 2× I2C, 2× UART, 4× 12-bit ADC, 16× controllable PWM channels
Accurate clock and timer on-chip
Temperature sensor
Accelerated floating point libraries on-chip
8 × Programmable IO (PIO) state machines for custom peripheral support
Pin Mapping
Pads numbered anticlockwise from USB connector.
Pad |
Signal |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
1 |
GPIO26 |
ADC0 |
2 |
GPIO27 |
ADC1 |
3 |
GPIO28 |
ADC2 |
4 |
GPIO29 |
ADC3 |
5 |
GPIO24 |
|
6 |
GPIO25 |
|
7 |
GPIO20 |
Default TX for UART1 serial console |
8 |
GPIO5 |
Default RX for UART1 serial console |
9 |
GPIO6 |
|
10 |
GPIO4 |
|
11 |
GPIO3 |
|
12 |
3.3V |
Power out to peripherals. |
13 |
Ground |
|
14 |
5V |
The board has a STEMMA QT connector that is also connected to pins GPIO22 (I2C1 SDA) and GPIO23 (I2C1 SCL).
Power Supply
The Raspberry Pi Pico can be powered via the USB connector, or by supplying +5V to pin 14. The board had a diode that prevents power from pin 14 from flowing back to the USB socket, although this can be disabled by connecting on-board solder pads if there is need to run as a usb host.
The Raspberry Pi Pico chip run on 3.3 volts which is supplied by an on board regulator.
Installation & Build
For instructions on how to to install the build dependencies and create a NuttX image for this board, consult the main RP2040 documentation.
Configurations
All configurations listed below can be configured using the following command in
the nuttx directory (again, consult the main RP2040 documentation):
$ ./tools/configure.sh adafruit-qt-py-rp2040:<configname>
gpio
NuttShell configuration (console enabled in UART1, at 115200 bps) with GPIO examples.
nsh
Basic NuttShell configuration (console enabled in UART1, at 115200 bps).
nsh-flash
Basic NuttShell configuration (console enabled in UART0, at 115200 bps with SMART flash filesystem.
nshsram
NuttShell configuration (console enabled in UART1, at 115200 bps) with interrupt vectors in RAM.
smp
Basic NuttShell configuration (console enabled in UART1, at 115200 bps) with both ARM cores enabled.
usbnsh
Basic NuttShell configuration using CDC/ACM serial (console enabled in USB Port, at 115200 bps).